Family Amaryllidaceae
Synonyms: Alliaceae APNI*
Gilliesiaceae APNI*
Agapanthaceae APNI*
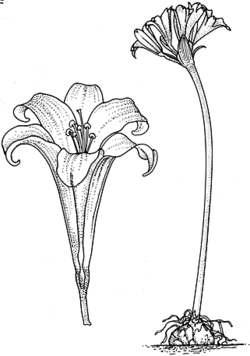
Description: Perennial herbs, with tunicated bulbs enclosed by membranous rather than fibrous scales or rarely rhizomes.
Leaves few, basal, ± linear, sheathing scape to varying heights, lamina with longitudinal veins ± parallel; stipules absent.
Inflorescences scapose, terminal, solitary or umbellate, mostly pedunculate, flowers solitary to many, subtended by an involucre of membranous, free or united bracts which initially enclose the flowers in bud. Flowers actinomorphic to slightly zygomorphic, 3-merous, bisexual, usually pedicellate. Perianth with or without tube; tepals or lobes 6 in 2 whorls, often persistent in fruit. Stamens 6, free or inserted on tube below lobes; filaments usually filiform, free or fused and forming corona; anthers 2-locular, epipeltate or basifixed, versatile, introrse, dehiscing by longitudinal slits or rarely apical pores. Ovary inferior, half-inferior, or superior, usually 3-locular or rarely 1-locular; placentation axile; styles slender with capitate or 3-lobed stigma.
Fruit a loculicidal capsule or fleshy and indehiscent; seeds few to numerous, often black and angular or subglobose, not winged.
Distribution and occurrence: World: c. 80 genera, c. 2100 species, mostly tropical & subtropical with some extending into temperate regions. Australia: c. 12 genera, 28 species, all States.
External links:
Angiosperm Phylogeny Website (Family: Amaryllidaceae, Order: Asparagales)
Wikipedia These genera have often been included in the Liliaceae s. lat. in the past. Many taxa are widely cultivated as ornamentals; these include species of Allium, Amaryllis, Clivia, Habranthus, Hippeastrum, Hymenocallis, Leucojum, Narcissus, Nerine, Pancratium and Zephyranthes. Allium and Nothoscordum are widespread weeds. Bulbs and fruit of some species are reported toxic to stock and humans if eaten. Amaryllidaceae has been expanded to include the onion family, Alliaceae, with Amaryllidaceae as the conserved name.
Text by G. J. Harden & N. Frischknecht (1993); D.C. Godden (1993); edited K.L. Wilson (Aug 2013) and R.L. Barrett (Nov. 2021)
Taxon concept: APG IV.
| | Key to the genera | |
| 1 | Flowers solitary | 2 |
| Flowers in umbels (2–30-flowered) | 5 |
| 2 | Flowers with a corona; perianth tube more than 10 mm long; scape solid; [perianth and corona yellow or perianth white and corona yellow or orange] | Narcissus |
| Flowers without a corona; perianth tube up to 12 mm long; scape hollow or solid
Back to 1 | 3 |
| 3 | Stamens of 4 different lengths; perianth bright yellow, orange-yellow or pink; flowers slightly zygomorphic, held slightly obliquely | Habranthus |
| Stamens of 2 different lengths; perianth mainly white or blue to purple, outer segments more or less tinged pink; flowers actinomorphic, held erect
Back to 2 | 4 |
| 4 | Perianth lobes to 16 mm long, blue with dark blue markings; tepals fused into a tube c. 12 mm long | Ipheion |
| Perianth lobes 30–50 mm long, mainly white; tepals free
Back to 3 | Zephyranthes |
| 5 | Scape strongly compressed; fruit a fleshy berry | Clivia |
| Scape round in cross-section; fruit a capsule
Back to 1 | 6 |
| 6 | Flowers with a corona | 7 |
| Flowers without a corona
Back to 5 | 9 |
| 7 | Perianth yellow, white, pink or purplish; corona yellow, orange or pink; leaves 0.5–2.5 cm wide | Calostemma |
| Perianth and corona white; leaves 2–35 cm wide
Back to 6 | 8 |
| 8 | Leaves strap-like; flowers sessile; perianth lobes 7–11 cm long | Hymenocallis |
| Leaves with ovate blade and petiole more than 10 cm long; flowers with pedicels 7–45 mm long; perianth lobes less than 2 cm long
Back to 7 | Proiphys |
| 9 | Tepals pink to mauve or blue | 10 |
| Tepals white (with green spots in Leucojum), yellow, orange or red
Back to 6 | 13 |
| 10 | Flowers appearing before the leaves emerge | Amaryllis |
| Flowers appearing after the leaves have emerged
Back to 9 | 11 |
| 11 | Tepals with wavy margins | Nerine |
| Tepals without wavy margins
Back to 10 | 12 |
| 12 | Tepals 40–45 mm long, (white or) pale to dark blue | Agapanthus |
| Tepals 90–100 mm long, (white or) pale pink to whitish
Back to 11 | Crinum |
| 13 | Perianth less than 2 cm long, tepals free or shortly fused, mostly white | 14 |
| Perianth more than 4 cm long, conspicuously tubular (or free in Agapanthus) but free part of tepals often recurved at maturity, white, yellow, orange-red or blue
Back to 9 | 16 |
| 14 | Tepals white with conspicuous greenish spot near apex of each tepal; anthers dehiscing by apical pores | Leucojum |
| 15
Back to | |
| 15 | Plants with an onion- or garlic-like odour when crushed; ovules usually 2 per loculus; style gynobasic | Allium |
| Plants with little or no onion- or garlic-like odour when crushed; ovules usually 4–12 per loculus; style terminal
Back to | Nothoscordum |
| Tepals orange-red with yellowish green bases
Back to 13 | Hippeastrum |
| 16 | Tepals white or pale yellow | 17 |
| 17 | Tepals 40–45 mm long, white (or pale to dark blue) | Agapanthus |
| Tepals 90–100 mm long, white (or pale pink to whitish)
Back to 16 | Crinum |
| | | |
|


