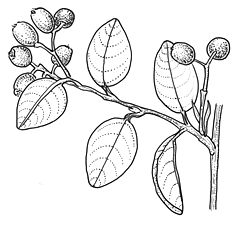
Description: Shrubs or seldom trees, evergreen or deciduous, often with pubescent or tomentose parts, branchlets never spiny.
Leaves simple and entire; petiole short; stipules present.
Flowers white or pink, appearing late in spring or summer after the leaves have developed; flowers solitary or in cymose clusters terminating short lateral spurs. Ovary inferior.
Fruit a pome, red, sometimes pruinose, pointed; 2–5-seeded.
Distribution and occurrence: World: 50 species, northern temperate regions. Australia: 6 species (naturalized), N.S.W., S.A.
At least 15 species are widely cultivated as ornamentals or as hedges, especially in cooler areas. Cotoneaster was formerly placed in the family Malaceae (now part of Rosaceae), e.g. Flora of New South Wales Vol. 1 (1990).
Text by G.J. Harden & A.N. Rodd
Taxon concept:
Taxa not yet included in identification key
Cotoneaster coriaceus,
Cotoneaster simonsii,
Cotoneaster x watereri
| | Key to the species | |
| 1 | Leaves more than 30 mm long | Cotoneaster glaucophyllus |
| Leaves less than 30 mm long | 2 |
| 2 | Leaves mostly more than 15 mm long, lower surface tomentose, not glabrescent with age | 3 |
| Leaves usually less than 15 mm long, lower surface with appressed hairs, glabrescent with age
Back to 1 | 4 |
| 3 | Leaves 12–25 mm long, veins inconspicuous on upper surface; fruit dull red | Cotoneaster pannosus |
| Leaves 20–35 mm long, veins deeply impressed on upper surface; fruit orange-red
Back to 2 | Cotoneaster franchetii |
| 4 | Leaves generally less than 10 mm long; petiole less than 2.5 mm long; plants often semiprostrate | Cotoneaster microphyllus |
| Most leaves 10–15 mm long; petiole more than 3 mm long; plants generally erect
Back to 2 | Cotoneaster rotundifolius |
|


