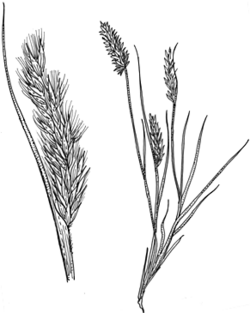
Description: Slender, tufted perennials or annuals.
Leaves with ligule a rim of hairs; blade narrow, convolute or sometimes flat, rolled in bud.
Inflorescence a narrow, feathery, spike-like panicle, sometimes with cleistogamous spikelets borne in the lower leaf sheaths.
Spikelets solitary, pedicellate, with the rachilla disarticulating above the glumes, 3–6 florets, the lower 1–3 bisexual, the upper smaller, sterile or rudimentary, sometimes reduced to awns only. Glumes 7–30-nerved, acute to obtuse, glabrous or pubescent. Lemmas rounded on the back, stiff, smooth or ribbed, hairy or glabrous, 9-nerved with the nerves continuing into 9 plumose, equal awns spreading at maturity. Paleas longer than the body of the lemma, 2-keeled, the keels ciliate near the margin.
Distribution and occurrence: World: c. 30 species, tropical & subtropical regions, especially Australia and Central & South America. Australia: 20 species (native), all mainland States.
Text by S. W. L. Jacobs & S. M. Hastings
Taxon concept:
| | Key to the species | |
| 1 | Hairs on the back of the basal lemma distinctly exceeding the base of the awns and obscuring the body of the lemma which is thickened and flattened on the surface, nerves not prominent | 2 |
| Dorsal hairs of basal lemma not exceeding the base of the awns (although a few hairs sometimes longer), the body of the lemma partly exposed (in some specimens the body of the lemma sometimes almost obscured); lemma thickened and flattened | 4 |
| 2 | Florets usually 5 or 6, only 1 fertile, body of lowest lemma longer than broad; glumes usually with 11 nerves or less | Enneapogon polyphyllus |
| Florets usually 3–5 with 2 or 3 fertile, body of lowest lemma as long as or shorter than broad; glumes usually more than 11-nerved
Back to 1 | 3 |
| 3 | Glumes with more than 13 nerves; fertile florets usually 2 or 3; awns more than 7–11 mm long | Enneapogon avenaceus |
| Glumes 7–16-nerved; fertile florets 2 (rarely 1); awns usually less than 7 mm long
Back to 2 | Enneapogon intermedius |
| 4 | Body of lemma with appressed hairs borne on the entire surface | Enneapogon virens |
| Body of lemma with spreading or erect hairs usually borne on the lower half
Back to 1 | 5 |
| 5 | Culms disarticulating at the nodes; axillary inflorescences present in the upper leaf sheaths | Enneapogon cylindricus |
| Culms not disarticulating at the nodes; axillary inflorescences absent
Back to 4 | 6 |
| 6 | Body of basal lemma thickened, nerves not or only partly ribbed but sometimes obvious because of their colour; glumes 7–15-nerved | Enneapogon gracilis |
| Body of basal lemma not thickened, nerves ribbed and prominent; glumes 5–7-nerved
Back to 5 | 7 |
| 7 | Awns to 2.5 mm long, about the same length as the lemma body; inflorescence dense and usually less than 2 cm long | Enneapogon lindleyanus |
| Awns more than 2.5 mm long and longer than the lemma body; inflorescence dense, moderately open and usually more than 2 cm long
Back to 6 | 8 |
| 8 | Body of lowest lemma deeply ribbed; palea longer than the lemma by c. 1 mm, the keels ciliate or scaberulous for all their length | Enneapogon truncatus |
| Body of lowest lemma only moderately ribbed; palea subequal to its lemma, the keels partly glabrous; (a variable species)
Back to 7 | Enneapogon nigricans |
|


